In today’s data-driven world, the phrase “Big Data” has become more than just a buzzword; it has evolved into a critical asset for businesses and industries across the globe. Big Data refers to the vast volume of structured and unstructured information generated through various sources such as social media, internet activities, sensors, and transactions. Leveraging this massive amount of data has proven to be a game-changer, revolutionizing the way organizations make informed decisions, uncover valuable insights, and drive innovation like never before.
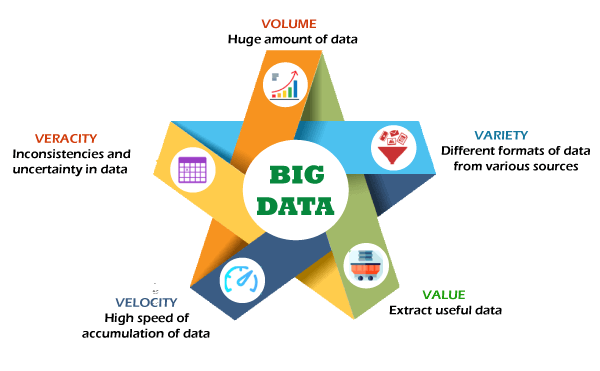
Potential of Big Data
1. The Era of Data Explosion:
Over the past decade, there has been an explosion of data production, and it continues to grow exponentially. The proliferation of smartphones, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and online platforms has contributed to the generation of an unimaginable amount of data every second. This data, when harnessed effectively, holds the potential to unlock new possibilities and fuel unprecedented advancements.
2. Unleashing Insights with Advanced Analytics:
Big Data analytics plays a pivotal role in extracting meaningful insights from the vast data ocean. With cutting-edge technologies like machine learning and artificial intelligence, businesses can now process and analyze data at lightning speed, identifying patterns, trends, and correlations that would have remained hidden otherwise. These insights enable organizations to make data-driven decisions, optimize processes, and enhance customer experiences.
3. Transforming Industries with Data-Driven Innovation:
The impact of Big Data is evident across various industries, driving innovation and disrupting traditional practices. In healthcare, data analytics has revolutionized patient care, diagnosis, and treatment plans, leading to better outcomes and reduced costs. In finance, data-driven algorithms power personalized financial services, fraud detection, and risk assessment. Manufacturing, retail, and marketing industries have also embraced Big Data analytics to enhance supply chain efficiency, customer targeting, and product recommendations.
4. Personalization and Customer Experience:
Big Data has transformed how companies interact with their customers. With access to extensive customer data, businesses can create personalized experiences tailored to individual preferences and behaviors. From targeted advertisements to personalized recommendations, Big Data enables companies to engage customers in more meaningful ways, building long-lasting relationships and brand loyalty.
5. Predictive Analytics and Forecasting:
One of the most valuable aspects of Big Data is its predictive capabilities. By analyzing historical data and real-time information, organizations can forecast future trends, demand patterns, and potential risks. This foresight empowers businesses to proactively respond to challenges and seize opportunities, optimizing operations and resources.
6. Challenges and Ethical Considerations:
While Big Data brings tremendous benefits, it also raises challenges related to data privacy, security, and ethics. Collecting and processing vast amounts of personal data necessitate stringent data protection measures to safeguard individuals’ privacy. Moreover, ethical considerations surrounding data usage and biases in AI algorithms must be carefully addressed to ensure responsible and fair use of Big Data.
In this section, we will explore the key challenges related to data privacy, security, and ethical considerations in the realm of Big Data.
- Data Privacy and Security:
As the volume of data grows, so does the concern for data privacy and security. Collecting vast amounts of personal information necessitates robust measures to protect individuals’ sensitive data from breaches and misuse. Companies and organizations handling Big Data must prioritize data protection, employ robust encryption methods, and ensure strict access controls to safeguard the privacy of their users. Additionally, adhering to regulatory frameworks, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), is crucial in maintaining the trust of customers and stakeholders.
- Ethical Data Usage:
Ethical considerations in Big Data revolve around how data is collected, used, and shared. It is essential to ensure that data collection practices are transparent and that individuals give informed consent for their data to be used. Companies must use data for legitimate purposes and avoid unauthorized or unethical data exploitation. Ethical guidelines should govern data usage, particularly when it comes to sensitive information, such as medical records or financial data, to prevent potential harm to individuals.
- Addressing Biases in AI Algorithms:
Big Data is often employed to train artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, making it crucial to address biases in data and algorithms. Biases can inadvertently seep into AI models, leading to discriminatory or unfair outcomes. For example, if historical data used for training AI contains biases, the AI may perpetuate those biases in its decision-making process. It is vital for data scientists and AI developers to actively identify and rectify such biases to ensure that AI systems are fair and unbiased in their assessments.
- Data Governance and Compliance:
As data is gathered from multiple sources, ensuring proper data governance and compliance becomes challenging. Organizations must establish clear guidelines for data handling, data retention, and data sharing to ensure compliance with relevant regulations and industry standards. Implementing strong data governance practices not only mitigates legal risks but also fosters trust with customers and stakeholders.
- Balancing Innovation and Responsibility:
Embracing the potential of Big Data and fostering innovation should go hand in hand with responsible practices. Striking the right balance is essential to ensure that the benefits of Big Data do not come at the expense of individuals’ privacy or perpetuate societal inequalities. Organizations should adopt a responsible data strategy that considers the ethical implications of their actions and promotes a culture of data ethics within their workforce.
The power of Big Data in uncovering insights and driving innovation is undeniable. From powering predictive analytics to revolutionizing industries, Big Data has become a catalyst for growth and transformation. Embracing this data-driven revolution and adopting responsible practices will enable organizations to harness the full potential of Big Data and navigate the future with confidence.



